Deformation of soft particles with controlled elasticity by liquid–liquid interfacial tension
-
chair:
Sapotta, B. / Kim, J. Q. / Willenbacher, N. / Choi, S. Q. (2019)
-
place:
Soft Matter, 2019,15, 4609-4613
- Date: Mai 2019
Abstract
Herein we report the deformation of PDMS-based particles at a liquid–liquid interface at varying degrees of softness. Direct visualization of the particle adsorption to the interface reveals at least five different modes of deformation from the complete spreading of a polymer resin droplet to a non-deforming, rigid particle.
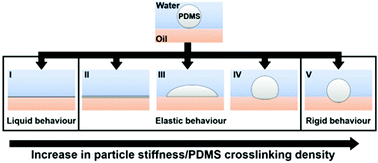
Pickering emulsions exploit the adsorption of particles to energy intensive liquid–liquid interfaces as a means to achieve interfacial stabilization. The stabilization effect increases with the amount of interfacial area covered by each individual particle. Therefore, the stabilization effect is maximized if a spherical particle is equally submerged into both liquid phases, which is commonly referred to as the neutral wetting state and depends on the wetting characteristics of the particle surface

