NEXAFS-Spectroscopy at Interfaces
The method of near-edge X-ray Absorption Fine Structure (NEXAFS) is used to study the electronic structure of organic adsorbents on metal surfaces and metal oxide surface.
The absorption of X-rays through matter near-nucleus excites electrons into unoccupied molecular orbital. The excitation occurs by emission of Auger electrons which are multiplied by inelastic scattering processes in the sample. The resulting Auger electrons can be detected using a detector. From near edge X-ray absorption fine-structure (NEXAFS) measurements, it is possible to gain insights on molecular orientations and bonding of the adsorbents to the surface.
The excitation of core electron into unoccupied orbitals requires synchrotron radiation of a very high intensity and good polarization (> 90%).
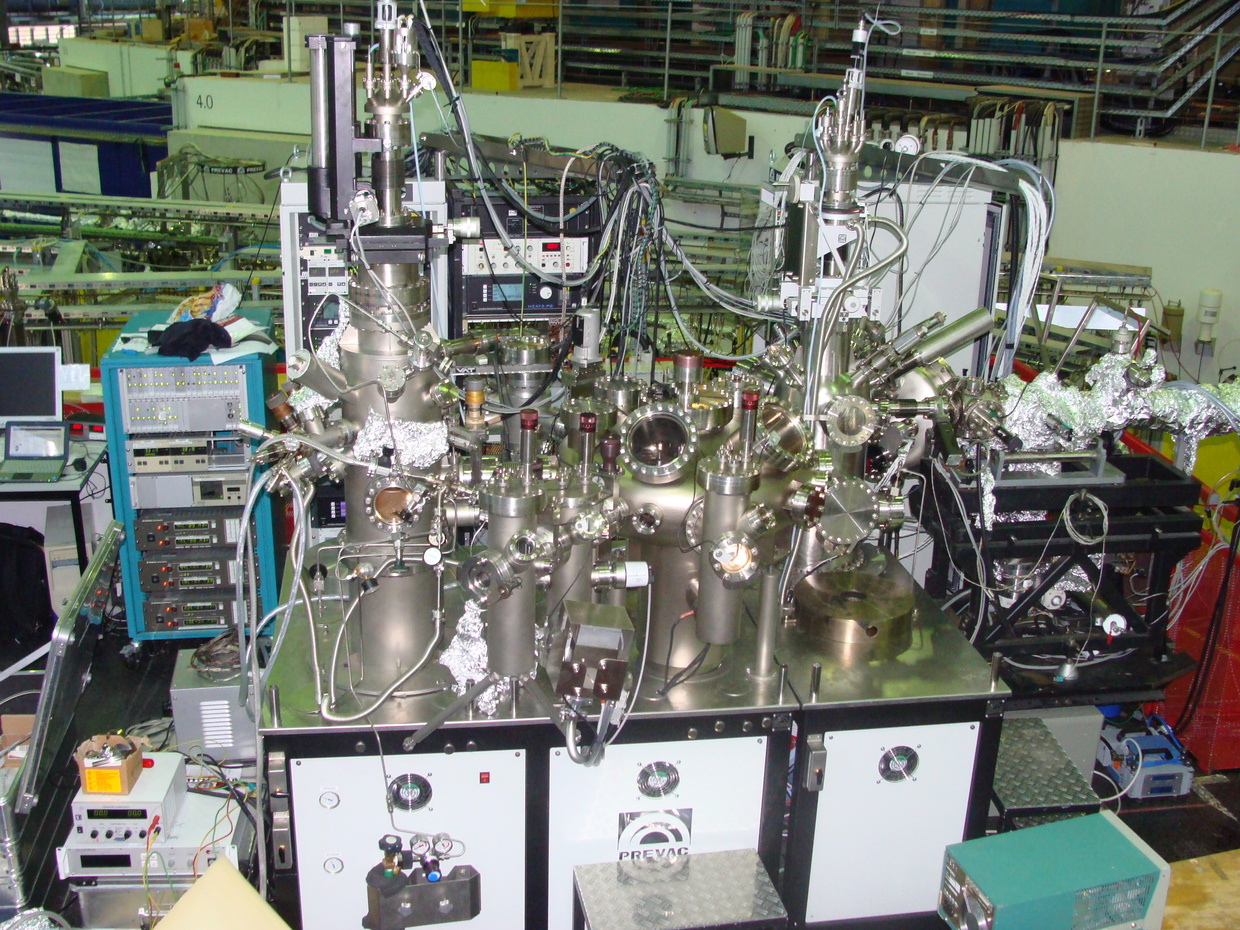
The apparatus used by us to measure NEXAFS spectra is additionally equipped with complimentary surface analytical techniques, namely XPS/UPS, low energy electron diffraction (LEED) and thermal desorption spectroscopy (TDS). Especially for more complex systems the possibility to characterize samples by other methods has been shown to be crucial for providing a unique and reliable interpretation of the experimental NEXAFS data. It consists of the analysis chamber for NEXAFS/XPS measurements, the preparation chamber equipped by evaporators, ion sputter guns and LEED system, a sample transfer system, including the distribution chamber with the park-station and two load lock chambers.
One of the load lock chambers is designed for a use of a special transport box, which allows transferring samples to other systems under UHV conditions. A crucial point is the sample transfer system which at the same time allows carrying out measurements in an extended temperature region. With the present setup samples can be investigated in a temperature region of at least 50—1000 K. This NEXAFS/XPS apparatus was designed and built by PREVAC (Poland) and is operated at the HESGM beamline of synchrotron facility BESSY II (Berlin, Germany). A photo of the setup is presented in Figure.
More information about near-edge X-ray Absorption Fine Structure (NEXAFS) can be found here.

NEXAFS-system at BESSYII
| Title | Author | Source |
|---|---|---|
| Self-Assembled Monolayers of Perfluoroanthracenyl-aminoalkane Thiolates on Gold as Potential Electron Injection Layers | Zhang, Z. / Wächter, T. / Kind, M. / Schuster, S. / Bats, J. W. / Nefedov, A. / Zharnikov, M. / Terfort, A. (2016) |
ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces,(2016), 8, 11, 7308–7319, |
| Atomically precise semiconductor-graphene and hBN interfaces by Ge intercalation | Verbitskiy, N. / Fedorov, A. / Profeta, G. / Stroppa, A. / Petaccia, L. / Senkovskiy, B. / Nevedov, A. / Wöll, C. / Usachov, D. / Vyalikh, D. / Yashina, L. / Eliseev, A. / Pichler, T. / Grüneis, A. (2015) |
Sci Rep. (2015); 5: 17700 |
| Boron-Doped Graphene Nanoribbons: Electronic Structure and Raman Fingerprint | Senkovskiy, B. V. / Usachov, D. Y. / Fedorov, A. V. / Marangoni, T. / Haberer, D. / Tresca, C. / Profeta, G. / Caciuc, V. / Tsukamoto, S. / Atodiresei, N. / Ehlen, N. / Chen, C. / Avila, J. / Asensio, M. C. / Varykhalov, A. Y. / Nefedov, A. / Wöll, C. / Kim, T. K. / Hoesch, M. / Fischer, F. R. / Grüneis, A. (2018) |
ACS Nano, 2018,12, 8, 7571-7582
|
| Metal–Support Interactions of Platinum Nanoparticles Decorated N-Doped Carbon Nanofibers for the Oxygen Reduction Reaction | Melke, J. / Peter, B. / Habereder, A. / Ziegler, J. / Fasel, C. / Nefedov, A. / Sezen, H. / Wöll, C. / Ehrenberg, H. / Roth, C. (2016) |
ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces,(2016), 8, 1, 82–90, |
| Surfactant modified platinum based fuel cell cathode studied by X-ray absorption spectroscopy | Melke, J. / Dixon, D. / Riekehr, L. / Benker, N. / Langner, J. / Lentz, C. / Sezen, H. / Nefedov, A. / Wöll, C. / Ehrenberg, H. / Roth, C. (2018) |
Journal of catalysis, 2018, 364, 282–290 |
| Chemical Properties of Metal-Silicates Rendered by Metal Exchange Reaction | Longo, R. C. / Königer, F. / Nefedov, A. / Thissen, P. (2019) |
ACS Sustainable Chem. Eng., 2019, 7, 9, 8449-8457 |
| Surface properties and graphitization of polyacrylonitrile based fiber electrodes affecting the negative half-cell reaction in vanadium redox flow batteries | Langner, J. / Bruns, M. / Dixon, D. / Nefedov, A. / Wöll, C. / Scheiba, F. / Ehrenberg, H. / Roth, C. / Melke, J. (2016) |
doi:10.1016 / j.jpowsour, 2016, 321, 210-218 |
| Formation and Stability of Nontoxic Perovskite Precursor | Hafshejani, T. M. / Hohmann, S. / Nefedov, A. / Schwotzer, M. / Brenner-Weiss, G. / Izadifar, M. / Thissen, P. (2019) |
Langmuir 2019, 35, 49, 16217-16225, doi.org/10.1021/acs.langmuir.9b03037 |
| Thermally Driven Ag–Au Compositional Changes at the Ligament Surface in Nanoporous Gold: Implications for Electrocatalytic Applications | Haensch, M. / Graf, M. / Wang, W. / Nefedov, A. / Wöll, C. / Weissmüller, J. / Wittstock, G. (2020) |
ACS Appl. Nano Mater, 2020, 3, 3, 2197–2206, doi.org/10.1021/acsanm.9b02279 |
| Efficient gating of epitaxial boron nitride monolayers by substrate functionalization | Fedorov, A. / Praveen, C., S. / Verbitskiy, N., I. / Haberer, D. / Usachov, D. / Vyalikh, D., V. / Nefedov, A. / Wöll, C. / Petaccia, L. / Piccinin, S. / Sachdev, H. / Knupfer, M. / Büchner, B. / Fabris, S. / Grüneis, A. (2015) |
Phys. Rev. (2015) B 92, 125440(7) |
| Charge carrier mobilities in organic semiconductors: crystal engineering and the importance of molecular contacts | Bashir, A. / Heck, A. / Narita, A. / Feng, X. / Nevedov, A. / Rohwerder, M. / Müllen, K. / Elstner, M. /Wöll, C. (2015) |
Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., (2015), 17, 21988-21996 |
| Spectroscopic Studies of Tetrahydroxybenzene Adsorption on Metal Surfaces | Alexei Nefedov, / Bebensee, F. / Wöll, C. (2017) |
ECASIA 2017, Montpellier, France |
